Parts DesignCarry out detailed structural design and DMU analysis based on the input of the whole vehicle and styling. |
|
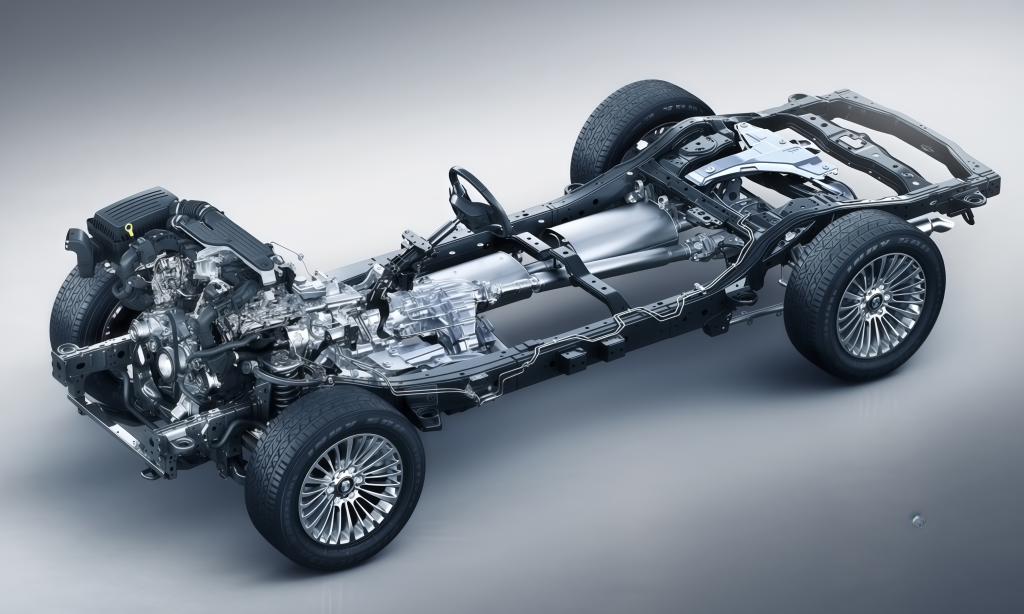 |
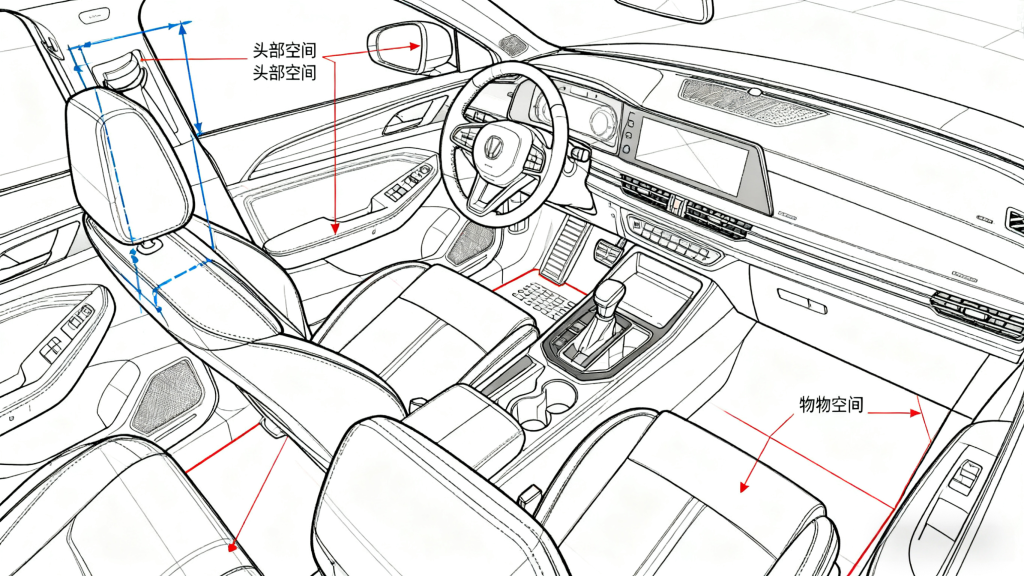
Chassis DesignSpatial arrangement of chassis system components Shift lever force analysis and verification Clearance verification of front and rear suspension movement Clearance verification of drive shaft movement Movement verification of sensor wiring harness Brake pedal movement analysis Steering system movement verification Tire package analysis Brake booster process analysis Movement verification of other system components |
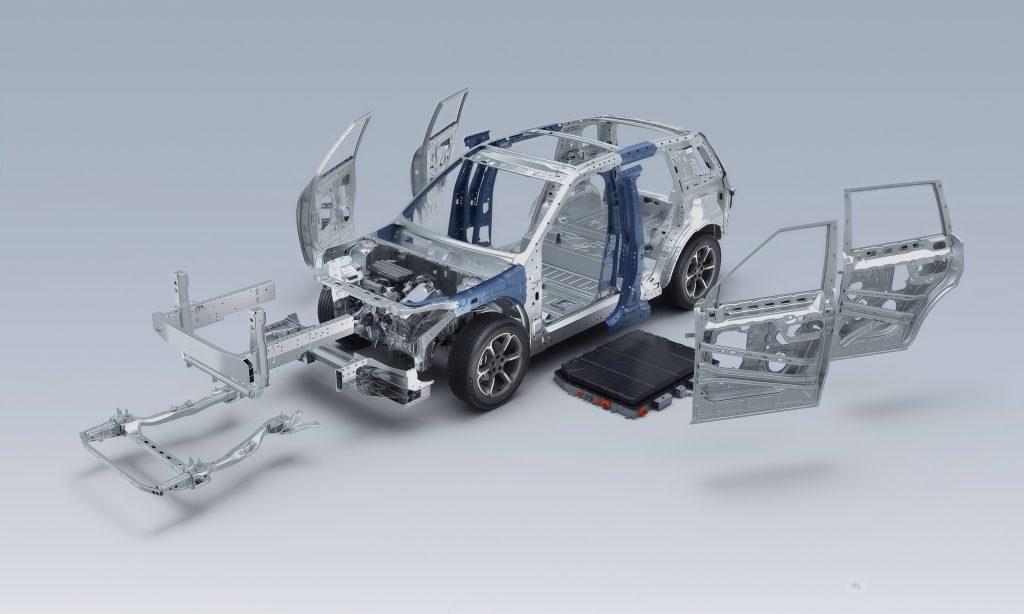
Body DesignMain section design Upper body structure design Lower body structure design Opening part structure design Front cabin structure design Movement verification of opening parts Delivery item production |
 |
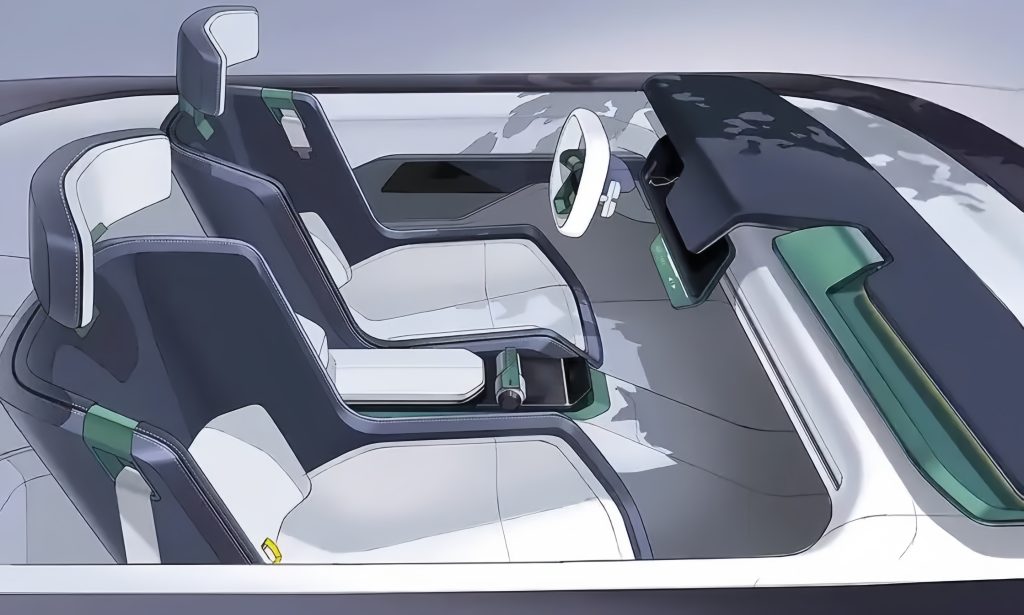 |
Interior and Exterior DesignStyling design Instrument panel system structure design Sub – instrument panel system structure design Door panel system structure design Door pillar system structure design Side wall system structure design Bumper structure design Roof structure design Engineering development Part manufacturing |
 |
|
 |
|
| Manufacturability Analysis | Stamping Process Design | CAE Accurate Analysis | Die Surface Processing | CNC machining | Mold Debugging | Verification after Commissioning |
| Evaluate the manufacturability of the automotive tooling design scheme from dimensions like production process, cost, and cycle, and identify potential manufacturing risks and issues in advance. | For automotive stamping parts, plan stamping procedures and determine process parameters such as the number of stamping times and mold structure, laying a process foundation for subsequent mold design. | Use computer-aided engineering technology to conduct mechanical, fluid, and other simulation analyses on automotive tooling (such as stamping molds), accurately predict tooling performance and product quality, and optimize the design. | Perform fine processing on the mold surface of automotive tooling molds to ensure the precision and finish of the mold surface, thereby guaranteeing the dimensional and surface quality of stamping parts. | Use numerical control equipment to perform high-precision and automated processing on the components of automotive tooling molds according to design requirements, ensuring the processing precision and consistency of parts. | Conduct trial molding and adjustment of the manufactured automotive tooling molds, solve problems such as mold jamming and poor part forming during the stamping process, and bring the molds to mass production status. | Conduct a comprehensive inspection of the automotive tooling molds after debugging, verify whether the dimensions, performance, appearance, etc., of the stamping parts meet the quality standards and production requirements. |